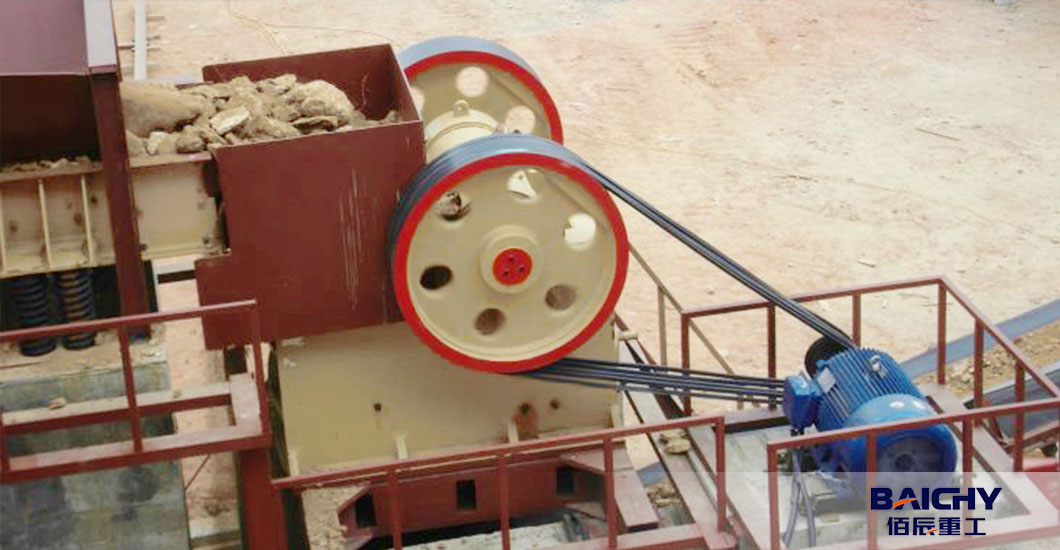
1. First Encounter with Jaw Crushers
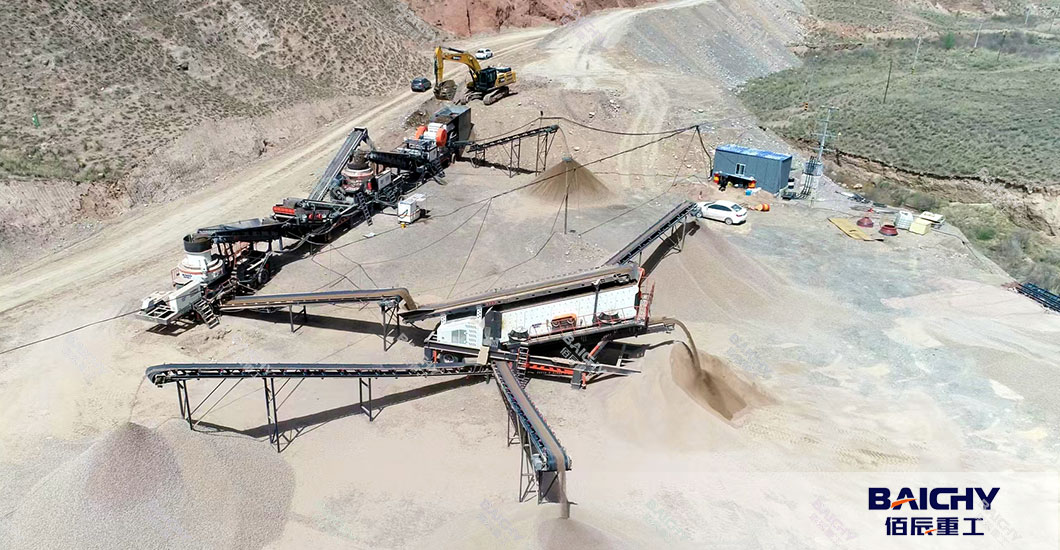
If you have ever passed by a construction site, a mine, or a quarry, you might have seen a huge steel machine chomping away at huge rocks, turning them into smaller pieces - that is likely to be a jaw crusher.
As the oldest and most fundamental member of the crushing equipment family, the jaw crusher has maintained its basic principle since it was invented by American Eli Whitney Blake in 1858. Its working mechanism is similar to that of a mechanical giant crocodile's lower jaw: a fixed "fixed jaw" and a periodically swinging "moving jaw" form a V-shaped crushing chamber, where rocks are crushed by being squeezed within this space.
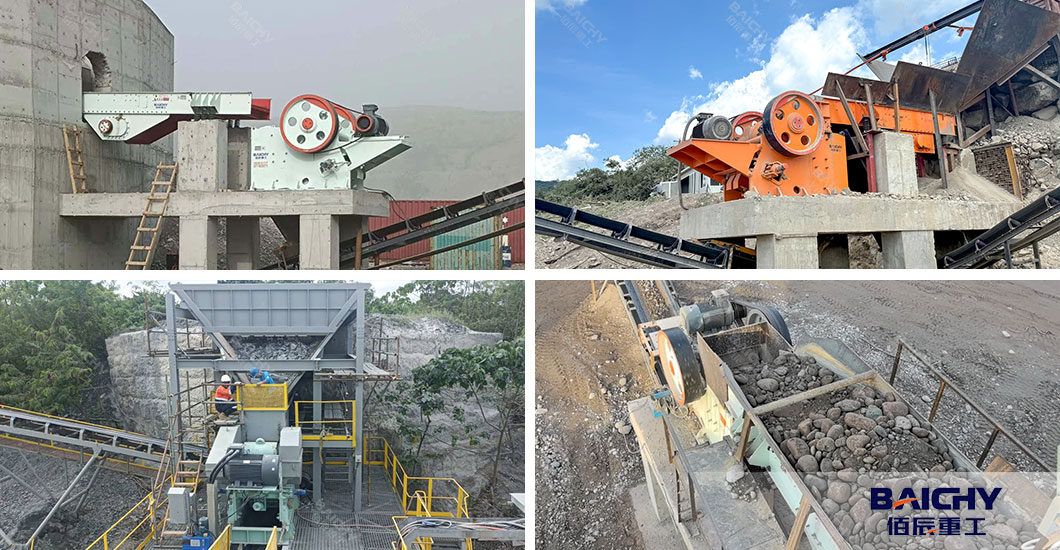

Why does the jaw crusher maintain such a long-lasting position among numerous crushing equipment? The answer lies in its unique combination of advantages. It can handle feed sizes ranging from 250 millimeters to 1500 millimeters. Materials with a compressive strength of up to 350 megapascals can also be processed smoothly. This means it can handle a wide variety of hard materials, from limestone to granite, from concrete blocks to iron ore.
Compared with other crushing equipment, the structure of the jaw crusher is simple and straightforward. It lacks complex hydraulic systems or high-speed rotating components, which makes it more durable and easier to maintain. It is particularly suitable as the first step in the crushing production line. In a typical crushing and screening process, the jaw crusher usually undertakes the "coarse crushing" task, reducing the raw materials to approximately 150-300 millimeters for preparing for the subsequent medium and fine crushing processes.
2. In-depth Analysis of Working Principle
Understanding the working principle of a jaw crusher is not complicated, but the mechanical intricacies within it are worth delving into. The entire process can be broken down into four key stages, each of which embodies the wisdom of mechanical engineering.
● When the materials enter the crushing chamber through the feed opening, they first come into contact with the inclined moving jaw plate. As the moving jaw approaches the fixed jaw, the materials are subjected to a gradually increasing compressive force. This stage is called the "initial engagement period". It is particularly important to note that in order to ensure that large pieces of materials can smoothly enter the crushing chamber, the width of the feed opening of the jaw crusher is usually 1.2-1.5 times the maximum processing size.
● As the moving jaw continues to move forward, the compressive force exerted on the material keeps increasing until it exceeds its compressive strength limit. At this point, the material begins to develop cracks and eventually breaks apart. This stage is called the "effective crushing period". During the crushing process, the material does not break completely at once but gradually disintegrates along natural cracks and weak surfaces. This characteristic makes the jaw crusher relatively energy-efficient.
● After being crushed, the materials move downward under the force of gravity. At the same time, during the return stroke of the moving jaw, they gain additional space to continue falling. Each time the moving jaw completes a forward and backward swing (referred to as a working cycle), a batch of materials is crushed and discharged. The working frequency of modern jaw crushers is usually between 250 and 500 times per minute, depending on the size and design of the equipment.
● The adjustment of the discharge port is a major feature of jaw crushers. By changing the position of the wedge-shaped blocks or gaskets, operators can precisely control the particle size of the products. This flexibility enables the same machine to produce products of different specifications, meeting various application requirements. The discharge port of a small jaw crusher can be adjusted to a minimum of 10 millimeters, while large equipment can handle discharges of 300 millimeters or more.
3. Main Types and Characteristics
Jaw crushers have various classification methods. Understanding these types and their characteristics will help in choosing the most suitable equipment for specific applications.
● According to the different movement trajectories of the moving jaw, jaw crushers can be classified into two major categories: simple pendulum type and compound pendulum type. The simple pendulum type (single pendulum type) has the moving jaw performing a simple circular arc swing around the fixed point. The advantage of this design is that the upper travel of the moving jaw is large, which is suitable for processing large pieces of hard materials, and the wear of the wear plates is relatively uniform. However, its structure is relatively complex, and the output is usually lower than that of the compound pendulum type equipment of the same specification.
The compound pendulum jaw crusher is the mainstream choice in the current market. Its moving jaw simultaneously participates in swinging and forward-backward movement, forming a more complex motion trajectory. This design increases the crushing efficiency by 20-30% compared to the simple pendulum type, resulting in more uniform product particle size and a more compact structure. However, the lower travel distance of the compound pendulum type may cause the lower wear plates to wear out faster, requiring more frequent maintenance.
● According to the installation method, jaw crushers can be classified as fixed type and mobile type. Fixed equipment is usually installed on concrete foundations, has a large processing capacity, and is suitable for long-term stable production environments. Mobile jaw crushers integrate feeders, conveyors, and diesel generator sets to form an independent mobile crushing station, which is particularly suitable for projects with scattered sites and short cycles, such as road construction or demolition sites of buildings.
● Modern jaw crushers have developed various variants based on the traditional design, such as hydraulic jaw crushers with hydraulic adjustment and overload protection functions, as well as deep-chamber jaw crushers that possess both coarse and medium crushing capabilities. These innovative designs have further expanded the application scope of jaw crushers, enabling them to adapt to more complex and variable working conditions.
4 Core Components
A jaw crusher is composed of multiple precisely-matched components, each of which plays an indispensable role. Understanding these components not only facilitates daily operations but also provides a foundation for fault diagnosis and maintenance.
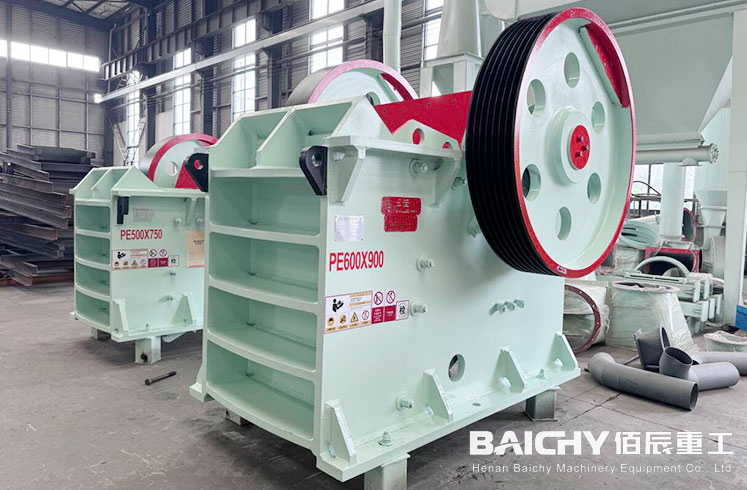
● The frame is the "skeleton" of the equipment, bearing all the working loads. Modern jaw crushers typically use high-quality steel plates for welding or cast steel components for manufacturing, featuring excellent strength and rigidity. The frames of large equipment can weigh several tons and require special attention to structural protection during transportation and installation processes.
● The moving jaw assembly is the "heart" of the equipment, consisting of key components such as the moving jaw body, shaft, bearings, and flywheel. The moving jaw body is usually made of cast steel, and its design directly affects the crushing efficiency. The flywheel's function is to store energy, accumulating kinetic energy during the idle period and releasing it during the working period to make the motor load more stable. A well-balanced flywheel can reduce equipment vibration and extend the lifespan of the bearings.
● The broken liner (jaw plate) is the part that comes into direct contact with the material and is the most prone to wear. The liner is usually made of high manganese steel or alloy steel, and its working surface is designed with longitudinal tooth patterns, which not only enhance the crushing effect but also extend the service life. Some advanced designs use symmetrical liners on the top and bottom. When the upper part wears out, it can be flipped over for use, effectively reducing the replacement cost.
● The adjustment device enables operators to change the size of the discharge port and control the particle size of the products. In the traditional method, a gasket is used for adjustment, which requires the equipment to be shut down for operation; modern equipment mostly adopts a hydraulic adjustment system, which can complete the adjustment while the equipment is running, significantly enhancing the production flexibility.
● The transmission system converts the rotational motion of the motor into the reciprocating motion of the moving jaw. Common transmission methods include belt transmission and direct transmission, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Belt transmission has a buffering effect, which can reduce the damage to the motor caused by impact loads, but requires more maintenance; direct transmission has higher efficiency and a more compact structure, but has higher requirements for the quality of the motor and reducer.

5 Application Areas and Selection Guide
The application scope of jaw crushers is astonishingly wide. From the most basic construction aggregate production to the most advanced mining processing, they can be seen everywhere. Choosing the appropriate jaw crusher lies in understanding the matching degree between one's own needs and the characteristics of the equipment.
● In the construction aggregate industry, jaw crushers are usually the first step in the production line. For common rocks such as limestone, granite or basalt, standard jaw crushers can meet the requirements. If the raw materials contain a lot of clay or moisture, a model with a larger inclination angle and special liner design may be needed to prevent blockages and adhesion.
● Mining applications have placed higher demands on jaw crushers. When processing hard iron ores or copper ores, the equipment needs stronger frames and more wear-resistant liners. Large mines usually opt for giant jaw crushers with a processing capacity exceeding 1000 tons per hour. Such equipment may require special foundation designs and installation plans.
● In the recycling industry, jaw crushers are widely used to process demolition waste and concrete blocks. In such cases, the equipment needs to be equipped with a steel bar cutting device and an iron protection system to prevent steel bars from getting tangled around the rotor or from unbreakable objects damaging the equipment. Mobile jaw crushers are particularly popular in this field because they can work directly at the demolition site, reducing the cost of material transportation.
When choosing a jaw crusher, multiple factors should be taken into consideration comprehensively: the characteristics of the materials (hardness, abrasiveness, moisture content), the required production capacity, the particle size requirements of the products, the installation site conditions, and the long-term operating costs. A common misconception is to overly focus on the initial purchase price while neglecting the energy consumption efficiency of the equipment, the lifespan of wear parts, and the ease of maintenance, as these factors often account for a larger proportion of the total life cycle cost of the equipment.
6 Maintenance and Safety Operations
Proper maintenance and operation of jaw crushers not only extends the equipment's lifespan but also ensures the safety of operators and the continuity of production. Adhering to standardized maintenance procedures and safety guidelines is of utmost importance.
● Daily inspections form the basis of preventive maintenance and should be conducted before each shift begins. Operators should check if fasteners are loose, if lubrication is adequate, if the wear of the liners is normal, and if there are any abnormalities in the transmission components. Special attention should be paid to the temperature of the moving jaw bearings; under normal circumstances, it should not exceed 70°C. Recording the data from daily inspections helps to identify potential problems and prevent sudden failures.
● The lubrication system is the "blood circulation system" of the jaw crusher and requires special attention. Bearings should use high-quality, high-temperature resistant lubricating grease, and be checked once every 8 hours. For large equipment, the automatic lubrication system can ensure the timeliness and accuracy of lubrication, but operators still need to regularly check the working condition of the system. It should be noted that different parts may require different types of lubricants, and the selection should strictly follow the manufacturer's recommendations.
● Replacing the liner plate is one of the most common maintenance tasks. When the tooth height wears down by more than 30-40% of its original height, it is advisable to consider replacing the liner plate. During the replacement process, it is necessary to check whether the supporting surface of the jaw body is flat and, if necessary, make adjustments. When tightening the liner plate bolts, one should follow the principle of cross symmetry and stepwise force application to ensure uniform force distribution.
● The safety operation procedures must be strictly followed. During equipment operation, it is strictly prohibited to open the observation door or make any adjustments; when clearing blockages, the machine must be stopped and the power disconnected first; warning signs and protective barriers should be set around the equipment. Operators should receive professional training to understand the working principle of the equipment and the emergency handling procedures. Regular safety drills can effectively enhance the team's ability to handle emergencies.
The world of jaw crushers is characterized by both the solid reliability of mechanical engineering and the continuous vitality of innovation. For beginners, understanding its basic principles and key points of operation and maintenance is the first step to entering this field. As experience accumulates, you will find that this seemingly simple machine contains countless ingenious designs and possibilities for optimization.
Relative Jaw Crusher Topics Maybe You Are Interested In
1. How do we analyze a jaw crusher machine?
2. How to Measure the Jaw Crusher Gap (CSS)?
3. How to operate a jaw crusher?
4. How to adjust jaw crusher gap?
5. Stone Jaw Crusher Machine: 6 Problems You Could Face
6. What Are The Parts Of Jaw Crushers?
7. What Are The Different Models And Specifications Of The Jaw Crusher
8. What are skills to buy jaw crusher
9. 3 Jaw Crusher Machine Alternatives
10.5 Tips to Maximize Jaw Crusher Efficiency and Productivity






 2026-01-21
2026-01-21

















 86-15093113821
86-15093113821
 86-15093113821
86-15093113821