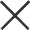
Jaw crushers are workhorses in mining, construction, and aggregates industries, tasked with breaking down large rocks into smaller, usable materials. But operating one safely and efficiently requires more than just flipping a switch. From pre-start checks to handling jams, every step impacts performance, equipment lifespan, and operator safety. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to operate a jaw crusher like a pro.
What Is a Jaw Crusher?
A jaw crusher uses a fixed jaw plate and a moving (swing) jaw plate to crush material. The moving jaw pivots back and forth, squeezing rocks between the two plates until they break into smaller pieces. It’s ideal for primary crushing—reducing large boulders (up to several feet in diameter) into manageable sizes for secondary processing or direct use (e.g., road base, concrete aggregate).
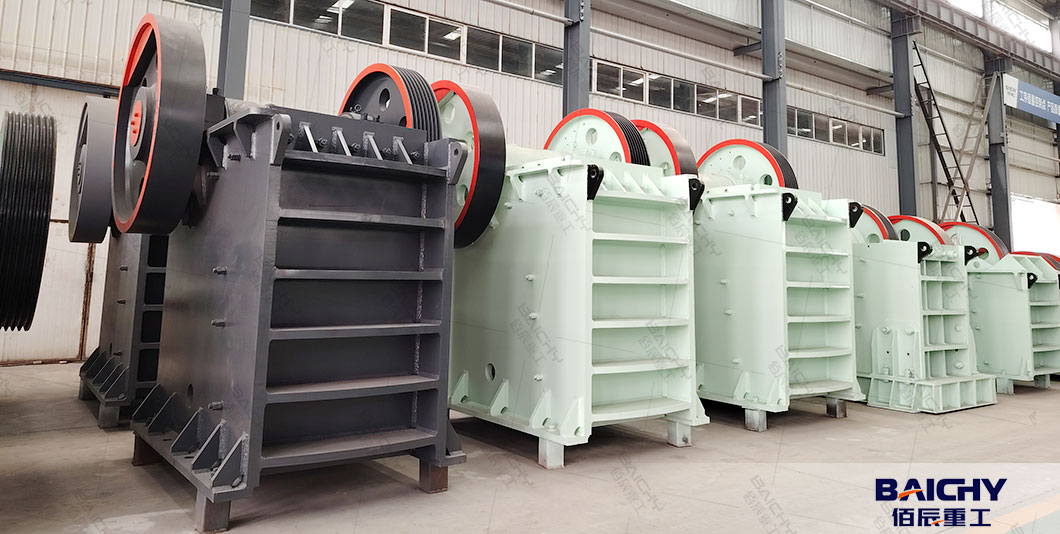

Why Proper Operation Matters
● Safety: Jaw crushers have powerful moving parts; improper use can lead to injuries or fatalities.
● Efficiency: Correct operation ensures consistent product size and maximizes throughput.
● Equipment Longevity: Avoiding overloads, jams, and uneven wear extends the life of jaw plates, bearings, and other critical components.
Step-by-Step Guide to Operating a Jaw Crusher
1. Pre-Start Checks: Prepare for Success
Never skip pre-start inspections. They catch issues before they turn into costly breakdowns or accidents.
● Safety First
- Ensure all safety guards (around the flywheel, crushing chamber, and drive belts) are intact and secured. Missing guards expose operators to moving parts.
- Test emergency stop buttons to confirm they work. They should immediately shut down the crusher if activated.
- Verify operators are wearing proper PPE: hard hats, safety glasses, steel-toe boots, hearing protection, and gloves.
● Mechanical Inspections
- Clear the crushing chamber: Remove any leftover rocks, metal scraps, or debris from previous use. Foreign objects can jam the crusher or damage jaws.
- Check jaw plates: Inspect for wear, cracks, or looseness. Rotate or replace plates if they’re unevenly worn—this ensures balanced crushing and longer life.
- Examine moving parts: Check the toggle plate, eccentric shaft, and linkage for cracks, rust, or excessive play. Tighten loose bolts.
- Inspect the drive system: Ensure V-belts are properly tensioned (no slippage) and aligned. Misaligned belts cause overheating and premature failure.
● Lubrication
- Check lubrication levels in bearings (eccentric shaft, toggle, and motor bearings) using sight glasses or dipsticks.
- Refill with the manufacturer-recommended lubricant (e.g., lithium-based grease) if low. Over-lubrication can attract dirt; under-lubrication causes friction and overheating.
cElectrical Checks
- Inspect power cords and connections for damage (fraying, corrosion). Loose connections cause voltage drops and motor issues.
- Confirm the power supply matches the crusher’s voltage requirements (e.g., 220V, 380V). Mismatched voltage damages the motor.
2. Startup: Get the Crusher Running Smoothly
Follow this sequence to start the crusher without stressing components:
● Clear the area: Ensure no one is near the crusher, feed hopper, or discharge conveyor. Post warning signs if needed.
● Start downstream equipment first: If the crusher is part of a processing line (e.g., with a conveyor or screen), start those first. This prevents material from piling up at the discharge.
● Start the crusher motor: Turn on the main power and start the motor. Let the crusher reach full operating speed *before* feeding material—this avoids overloading the motor.
● Set the Closed Side Setting (CSS): Adjust the gap between the jaws (CSS) to control output size. Use the crusher’s adjustment mechanism (wedges, hydraulics, or shims) as needed. Refer to our guide on [how to measure CSS](https://example.com/jaw-crusher-css) for accuracy.
3. During Operation: Monitor and Optimize
Once running, focus on consistent feeding and vigilance to keep the crusher efficient.
● Feeding Material
- Use a vibrating feeder to control the feed rate. Overfeeding clogs the chamber; underfeeding wastes energy.
- Distribute material evenly across the jaw width. Uneven feeding causes uneven jaw wear and inconsistent product size.
- Never feed material larger than the crusher’s maximum feed size (check the manual). Oversized rocks jam the chamber or crack jaws.
● Monitor Performance
- Listen for odd noises: Grinding, knocking, or screeching may signal a jam, loose parts, or foreign objects (e.g., steel). Stop immediately to investigate.
- Check bearing temperatures: Use an infrared thermometer to measure bearing heat. Most manufacturers recommend keeping temperatures below 180°F (82°C). Overheating means poor lubrication or a failing bearing.
- Inspect output size: Periodically check the crushed material. If it’s coarser or finer than desired, adjust the CSS (after stopping the crusher).
● Handling Jams
Jams happen, but improper handling risks injury. Do this:
- Stop the motor and lock out the power supply (use a padlock to prevent accidental restart).
- Wait for all moving parts to stop.
- Clear the jam manually with tools (e.g., a pry bar or sledgehammer). Never reach into the chamber with hands.
- Identify the cause (oversized material, uneven feeding) and fix it before restarting.
4. Shutdown: End the Shift Safely
Proper shutdown protects the crusher and makes the next start easier.
● Stop feeding material: Let the crusher empty the chamber—running empty prevents buildup.
● Shut down the crusher motor: Wait until the chamber is clear, then turn off the power.
● Stop upstream/downstream equipment: After the crusher stops, shut down feeders, conveyors, etc.
● Post-operation cleanup:
- Remove residual material from the chamber to prevent rust or hardening.
- Wipe down external surfaces to remove dust and debris.
- Secure the crusher with lockout/tagout if it won’t be used soon.
Pro Tips for Optimal Operation
● Train operators: Ensure everyone knows safety protocols and troubleshooting steps.
● Keep a log: Record start/stop times, maintenance checks, and issues (e.g., jams, wear). This helps spot patterns.
● Replace wear parts on schedule: Jaw plates, toggle plates, and bearings wear faster with heavy use. Replace them before they fail.
● Match material to crusher specs: Hard rocks (e.g., granite) need a different CSS than soft materials (e.g., limestone). Adjust accordingly.

Final Thoughts
Operating a jaw crusher safely and efficiently requires attention to detail—from pre-start checks to shutdown. By following these steps, you’ll reduce downtime, extend equipment life, and ensure consistent, high-quality output. Always refer to your crusher’s manual for model-specific guidelines, and prioritize safety above all else.
*Need help with maintenance or parts? Contact your manufacturer or a trusted supplier for support.*
People Also Frequently Ask For:
1.What are the disadvantages of jaw crusher?
Although jaw crushers work reliably, it disadvantage is output particle size is not so uniform . The size of the output particle size varies with jaw crusher model.
2.How do you increase the efficiency of a jaw crusher?
Ensure that the feed material is properly sized for jaw crusher, and avoid overloading the crusher with oversized material. Also it needs to control the feed speed to avoid overloading and ensure a steady, efficient flow of material through jaw crusher.
3.Why is my jaw crusher not working?
There are some items to check: jaw die and key/heel bolts are tight; bearings is broken; the thrust plate is broken; the connecting rod is damaged; the spring is broken;Repair or replace new part and start jaw crusher again.








 2026-01-13
2026-01-13


















 86-15093113821
86-15093113821
 86-15093113821
86-15093113821