The crushers used in quarry are heavy-duty machine designed to reduce large rocks, boulders, or ore into smaller, uniform particles. The main types of crushers are jaw crushers, impact crushers, and cone crushers. They work together, processing materials of varying hardness and moisture content through compression, impact, and grinding, achieving multi-stage crushing to meet the aggregate size requirements of different industries such as construction materials, highways, and railways.

1.The process of quarry crushing plant typically involves three stages:
● Primary Crushing: Reduces large boulders (up to 1.5 meters in diameter) to smaller rocks (10–30 cm).
● Secondary Crushing: Breaks primary-crushed rocks into medium-sized particles (2–10 cm).
● Tertiary Crushing: Refines particles into fine aggregates (0.5–2 cm) or specialized sizes for high-quality applications.
2. Key Types of Crushers Used in Quarries
Quarries use different types of crushers based on rock type, desired product size, and production capacity. Below are the most common types, each tailored to specific stages of the crushing process:
2.1 Jaw Crusher (Primary Crushing)
The jaw crusher is the workhorse of primary crushing in quarries. It features a fixed jaw plate and a moving jaw plate that oscillates to squeeze and crush rocks.
● Design: Simple, robust, and easy to maintain, with a V-shaped crushing chamber that accommodates large feed sizes (up to 1200mm).
● Best For: Limestone, granite, and sandstone quarries needing high-capacity primary crushing (10–1000 tons per hour, t/h).
● Advantages: Handles hard, abrasive rocks; low energy consumption; minimal downtime; ideal for large-scale quarries.
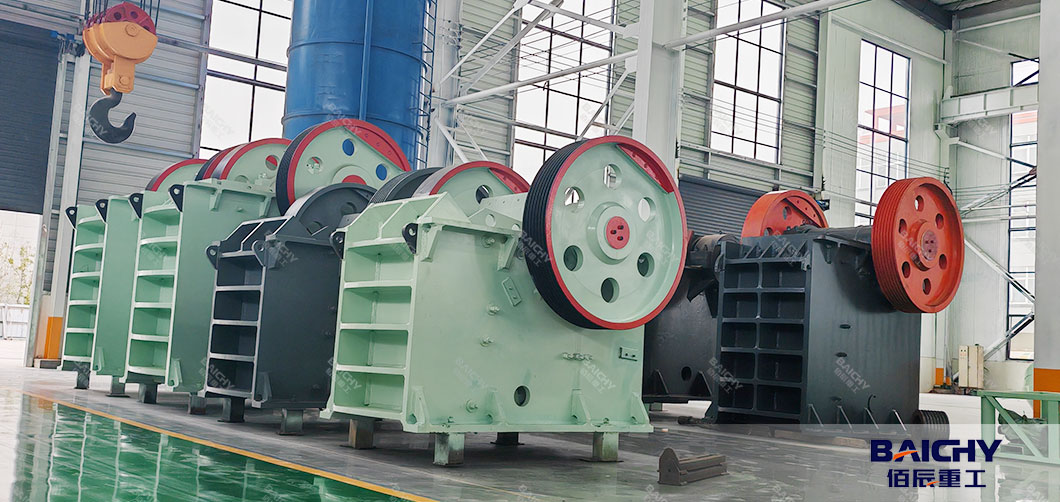

2.2 Impact Crusher (Secondary/Tertiary Crushing)
Impact crushers use high-speed rotating hammers or blow bars to strike rocks, breaking them by impact and rebound.
● Design: Two types—horizontal shaft impact (HSI) and vertical shaft impact (VSI) crushers. HSIs are for secondary crushing (reducing 10–30cm rocks to 2–10cm), while VSIs excel at tertiary crushing (producing cubic, fine aggregates).
● Best For: Quarries producing high-quality aggregates for concrete, asphalt, or road construction (e.g., basalt or limestone quarries).
● Advantages: Delivers uniform, cubic product shape; high crushing ratio; suitable for brittle or medium-hard rocks.
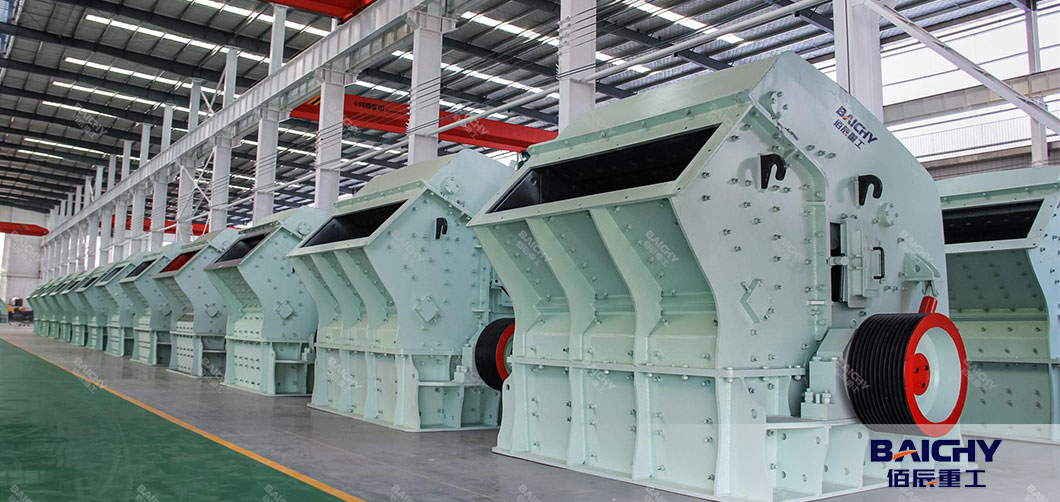

2.3 Cone Crusher (Secondary/Tertiary Crushing)
Cone crushers operate via a rotating cone that gyrates within a fixed concave chamber, crushing rocks by compression.
● Design: Available in standard, medium, or short-head configurations (for different product sizes). Modern models feature hydraulic adjustment and overload protection.
● Best For: Hard rock quarries (e.g., granite, basalt) requiring high-capacity, fine crushing (50–500 t/h) and consistent particle sizes.
● Advantages: Durable, energy-efficient; produces low needle-like content; ideal for large quarries with strict product quality standards.

2.4 Roll Crusher (Specialized Crushing)
Roll crushers use two rotating rolls to crush rocks by compression. They are less common in quarries but useful for specific applications.
● Design: Smooth or toothed rolls that rotate inward to squeeze rocks.
● Best For: Soft to medium-hard rocks (e.g., limestone, gypsum) or quarries needing narrow particle size ranges (e.g., 1–5cm).
● Advantages: Low noise, minimal dust; suitable for low-abrasion materials.

3.How to Choose the Right Crusher for Your Quarry
Selecting the optimal quarry crusher depends on four key factors:
3.1 Rock Type & Hardness
● Hard rocks (granite, basalt): Jaw crusher (primary) + cone crusher (secondary/tertiary).
● Medium-hard rocks (limestone, sandstone): Jaw crusher + impact crusher.
● Soft rocks (gypsum, shale): Roll crusher or small jaw crusher.
3.2 Desired Product Size & Quality
● Coarse aggregates (20–50mm): Jaw crusher (primary) only.
● Medium aggregates (10–20mm): Jaw + impact/cone crusher.
● Fine aggregates (1–10mm): Tertiary cone crusher or VSI.
● Cubic shape requirement: Impact crusher (VSI) is preferred.
3.3 Production Capacity
● Small quarries (10–50 t/h): Compact jaw crusher or mobile crusher.
● Medium quarries (50–200 t/h): Jaw crusher + cone/impact crusher.
● Large quarries (200+ t/h): Heavy-duty jaw crusher + multiple cone/impact crushers.
3.4 Budget & ROI
● Initial investment: Jaw crushers are cost-effective for primary crushing; cone/VSI crushers have higher upfront costs but better long-term efficiency.
● Operating costs: Consider energy consumption, wear part replacement, and labor. Energy-efficient models (e.g., hydraulic cone crushers) offer better ROI for high-volume operations.

4. Trends in Quarry Crushing Technology
The quarry crusher industry is evolving with innovative technologies to improve efficiency and sustainability:
● Mobile Crushers: Compact, transportable crushers (e.g., mobile jaw/cone crushers in wheel type or crawler type) allow quarries to process material on-site, reducing transportation costs.
● Intelligent Control Systems: stone crushers with real-time monitoring (temperature, pressure, throughput) optimize performance and reduce downtime.
● Eco-Friendly Designs: Crushers with low dust emissions and noise reduction meet strict environmental regulations.
If you’re looking to invest in a quarry crusher or upgrade your existing equipment, partner with a reputable supplier that offers durable, energy-efficient models and comprehensive after-sales support. With the right crusher, your quarry can meet growing demand for construction materials while minimizing costs and environmental impact.











 2026-01-05
2026-01-05


















 86-15093113821
86-15093113821
 86-15093113821
86-15093113821