A sand processing plant relies on a range of specialized equipment to transform raw sand (natural or crushed) into clean, graded, and market-ready products. The specific equipment used depends on the plant’s purpose (e.g., washing natural sand, producing manufactured sand, or removing impurities), but the following are typical pieces of equipment found in most configurations:
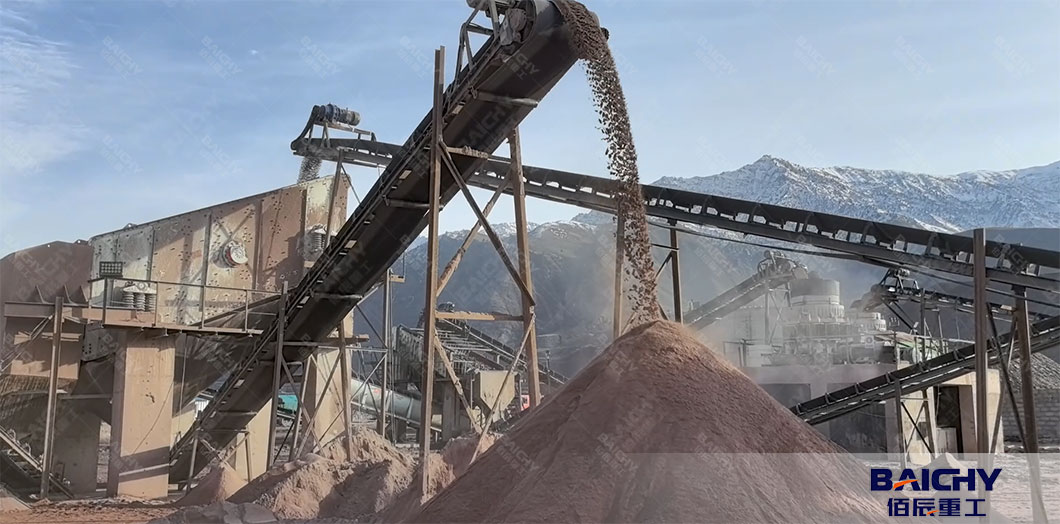

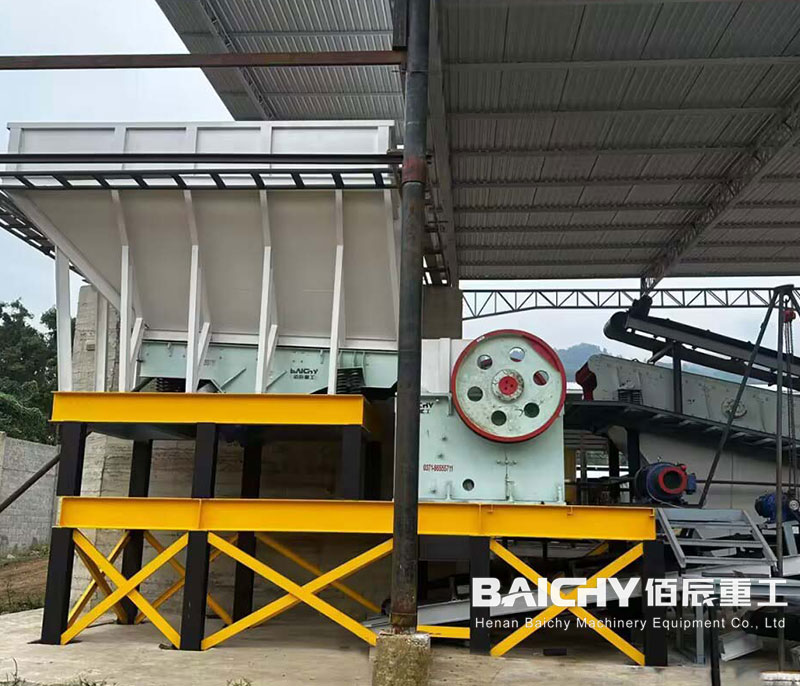
1. Feeding Equipment
These machines control the flow of raw material into the processing line, ensuring a steady and uniform supply to downstream equipment.
● Vibrating Feeder:
- Uses vibrating motors to convey bulk raw sand (or crushed stone for manufactured sand) from storage piles or hoppers to crushers, screens, or washers.
- Adjustable vibration intensity allows control over feed rate, preventing overloads in downstream equipment.
- Often paired with a grizzly bar (a grid of metal bars) to pre-screen large impurities (e.g., rocks, debris) before feeding.

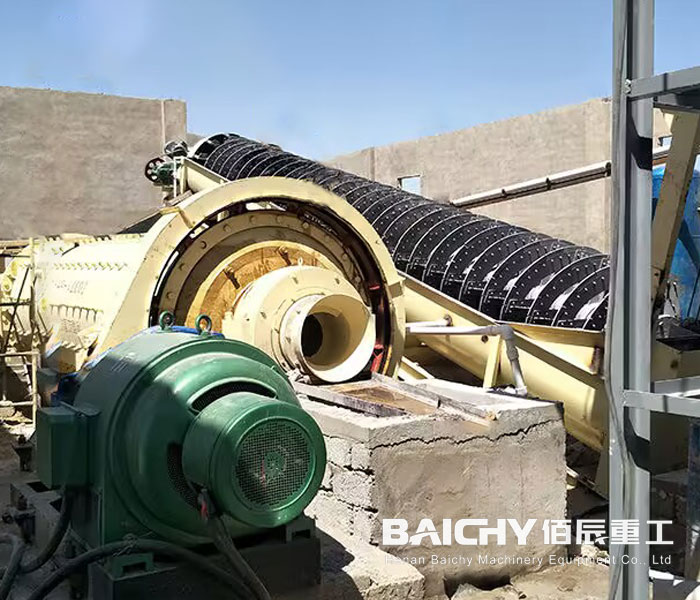
2. Crushing Equipment (For Manufactured Sand Production)
Manufactured sand (M-sand) requires crushing hard rocks (granite, basalt) into sand-sized particles. These crushers reduce rock size step-by-step:
● Jaw Crusher (Primary Crusher):
- Breaks large rocks (up to 1m in diameter) into smaller fragments (50–100mm).
- Uses a fixed "jaw" and a moving jaw to compress and crush material—ideal for hard, abrasive rocks.
● Cone Crusher (Secondary Crusher):
- Further reduces primary crushed material (50–100mm) to smaller sizes (10–30mm).
- Uses a rotating cone within a fixed concave chamber to crush material via compression—produces uniform, cubical particles.
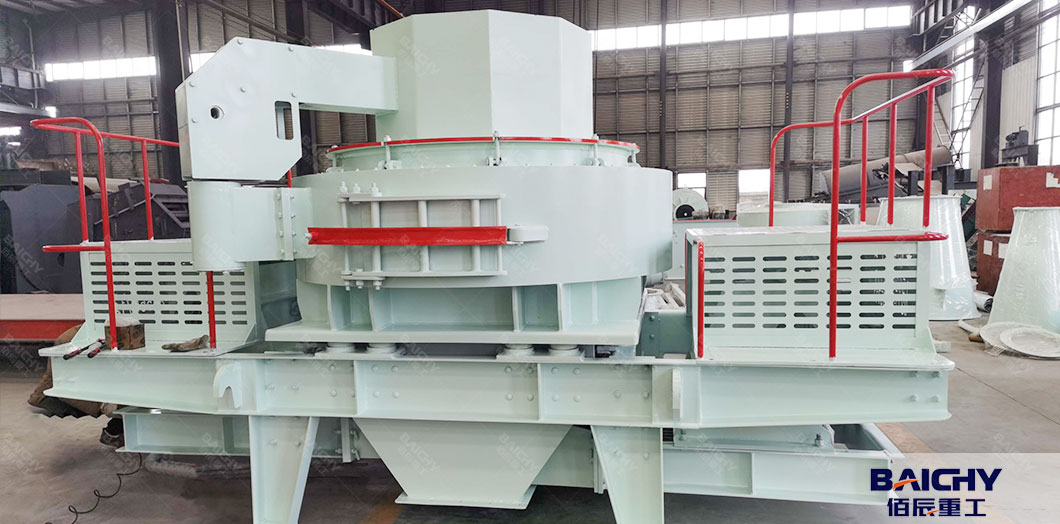
● Vertical Shaft Impactor (VSI Crusher, Tertiary Crusher):
- Critical for shaping M-sand: Reduces 10–30mm material to sand-sized particles (0–5mm).
- Uses high-speed rotating impellers to throw material against a crushing chamber, creating collisions that break particles into rounded, cubic shapes (reduces flaky particles, improving sand quality for concrete).

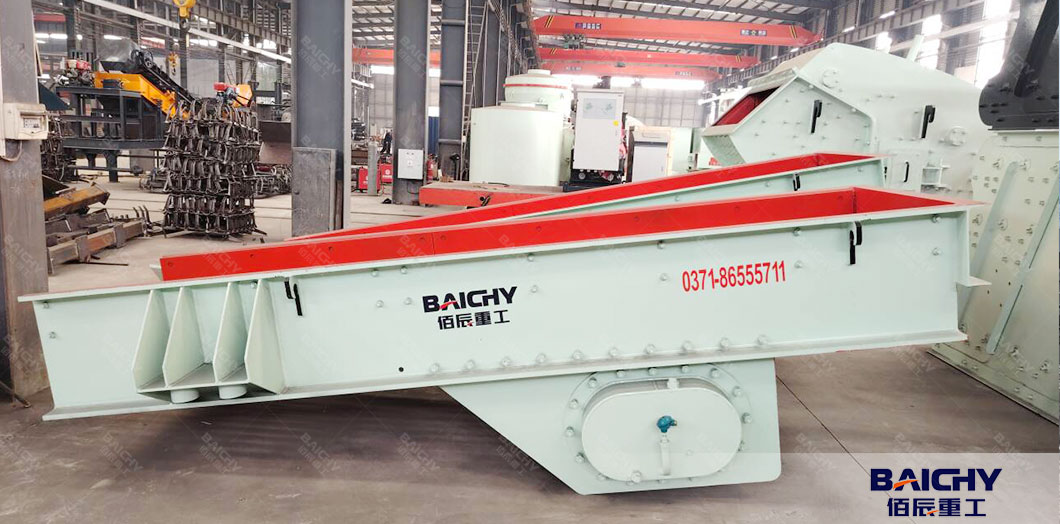
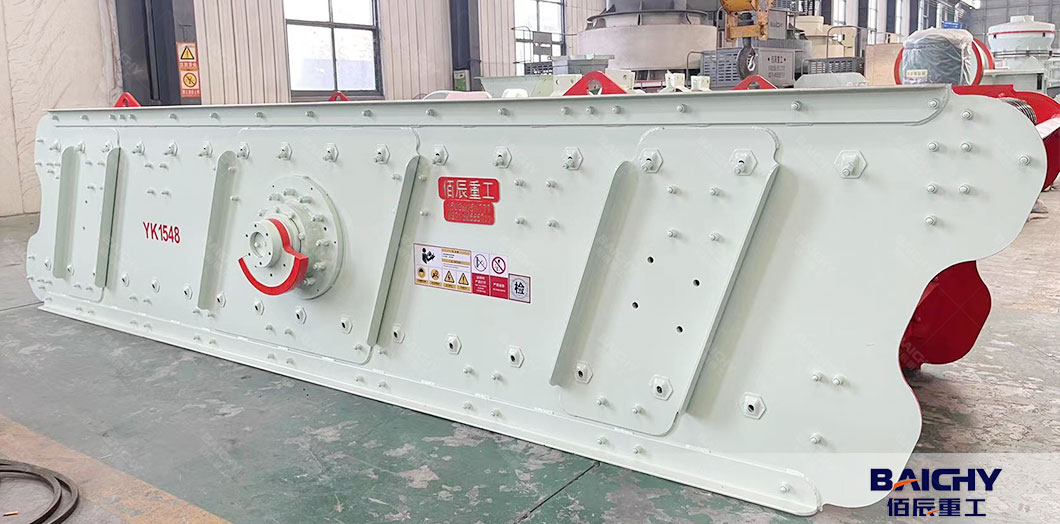
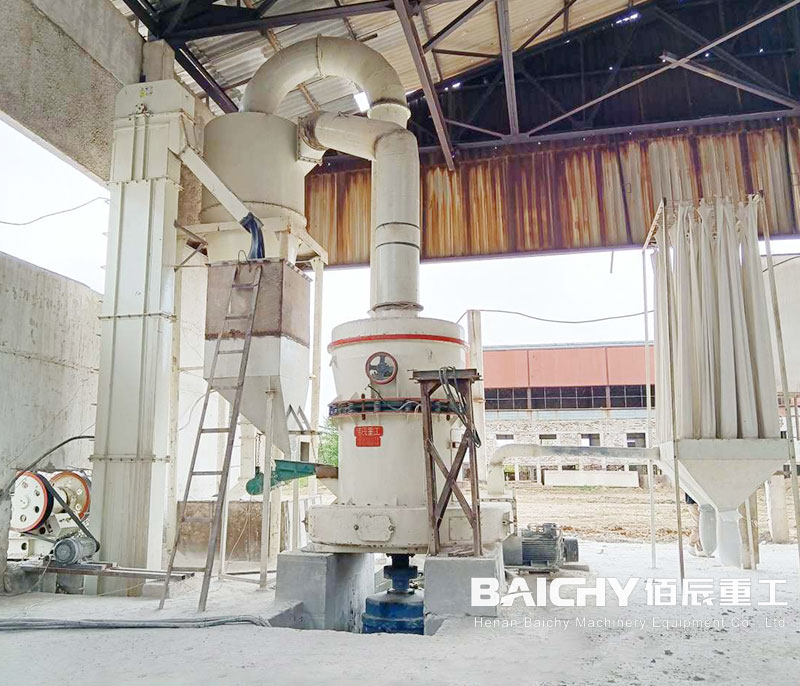
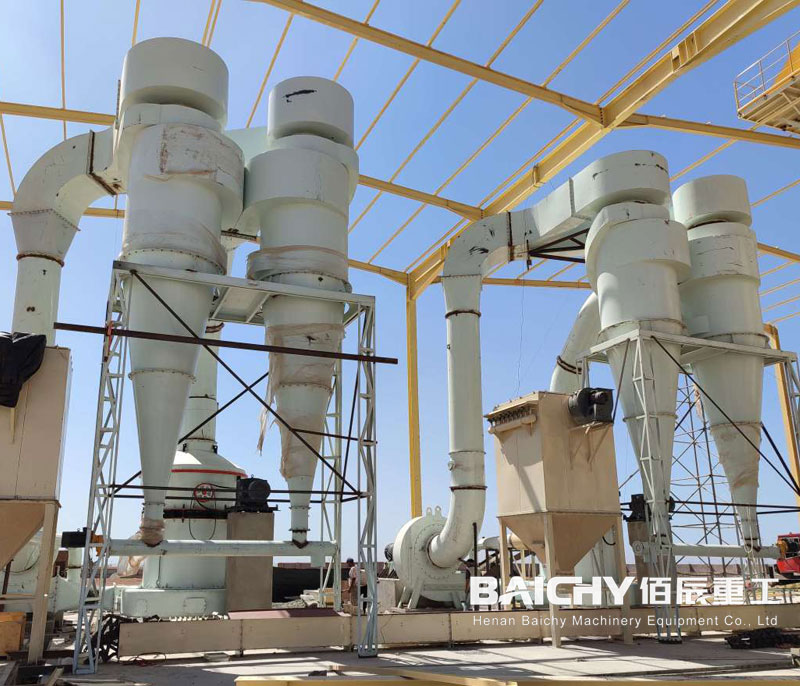
3. Screening Equipment
Screens separate sand into specific size fractions, remove oversize material, and ensure consistent grading.
● Vibrating Screen:
- A deck (or multiple decks) with mesh screens vibrates to separate particles by size.
- Common configurations: 1–3 decks with varying mesh sizes (e.g., 0.15mm, 1.18mm, 4.75mm) to produce graded sand (e.g., fine sand for mortar, coarse sand for concrete).
- Oversize particles (too large to pass through the mesh) are recycled back to crushers for reprocessing.
● Dewatering Screen:
- A specialized dewatering vibrating screen with a fine mesh and inclined design to remove excess water from washed sand.
- Reduces moisture content from ~20% (after washing) to 8–12%, making sand easier to store, transport, or use in dry applications.

4. Washing & Cleaning Equipment
These machines remove impurities (clay, silt, organic matter) from sand, critical for producing clean, high-quality products.
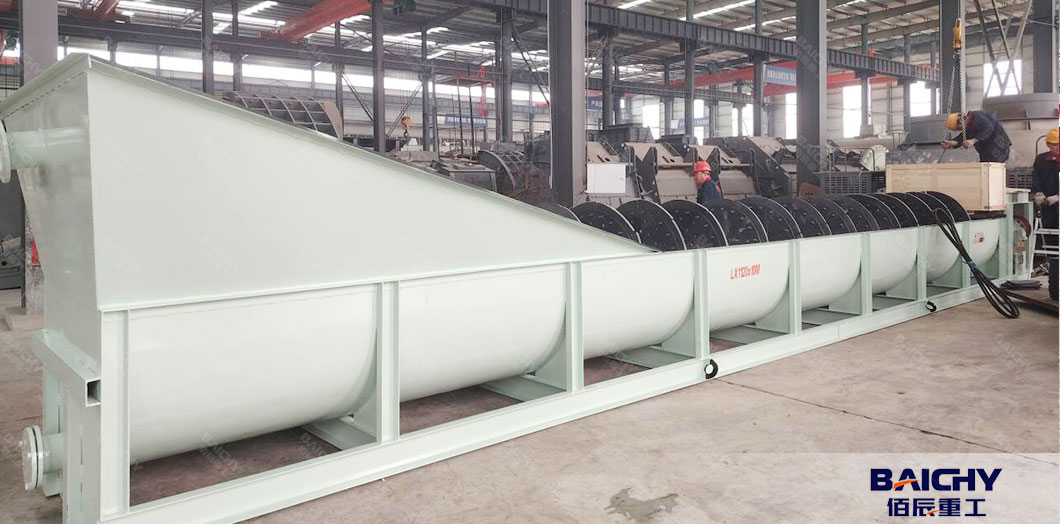
● Spiral Sand Washer:
- Spiral sand washing machine uses a rotating spiral blade within a tank filled with water.
- Sand is scrubbed by the spiral, and impurities (silt, clay) are carried away by water overflow.
- Efficient for removing fine silt—common in natural sand washing (e.g., river sand).
● Wheel Sand Washer (Bucket Sand Washer):
- Consists of a rotating wheel with buckets that scoop and agitate sand in water.
- Simplified design, lower water consumption, and easier maintenance than spiral washers.
- Suitable for sand with moderate impurity levels.
● Scrubber (Attrition Scrubber):
- Used for sand with stubborn clay coatings (e.g., pit sand).
- Agitates sand in a water-filled tank with paddles, breaking up clay lumps via friction before washing.

5. Impurity Removal Equipment
For sand with specific contaminants (e.g., iron, organic matter), specialized equipment targets and removes these impurities:
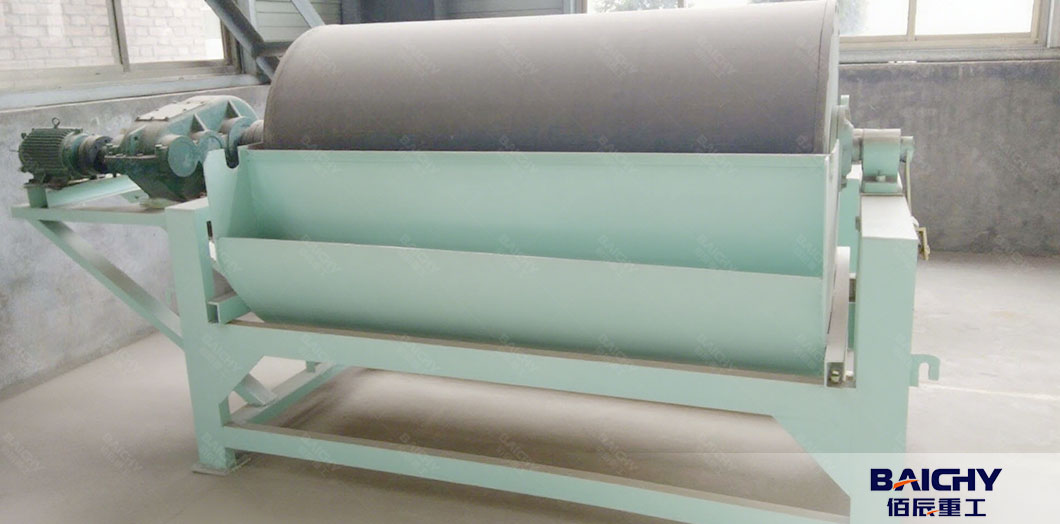
● Magnetic Separator:
- Uses strong magnets (electromagnets or permanent magnets) to attract and remove ferrous impurities (iron particles, nails).
- Essential for high-purity applications (e.g., glass manufacturing, electronics).
● Air Classifier:
- Uses controlled airflow to separate light impurities (organic matter, dust) from sand.
- Common in dry processing plants (water-scarce regions) as an alternative to water-based washing.
● Gravity Separator (Jig or Spiral Chute):
- Separates heavy non-ferrous impurities (e.g., pyrite, garnet) by density.
- Works by creating a pulsating water flow that lifts lighter sand particles while heavier impurities settle.

6. Dewatering & Drying Equipment
After washing, sand must be dried or dewatered to meet moisture requirements for storage and use.
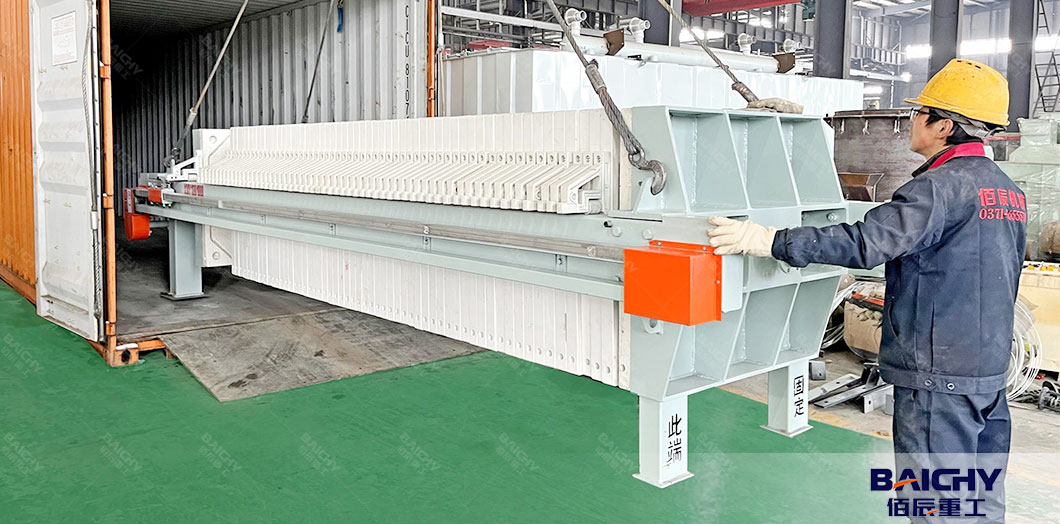
● Filter Press:
- Uses pressure to squeeze water out of sand slurry, producing dry cake-like sand with low moisture (~5–8%).
- Efficient for high-moisture slurries but slower than dewatering screens—often used for fine sand or sludge recovery.
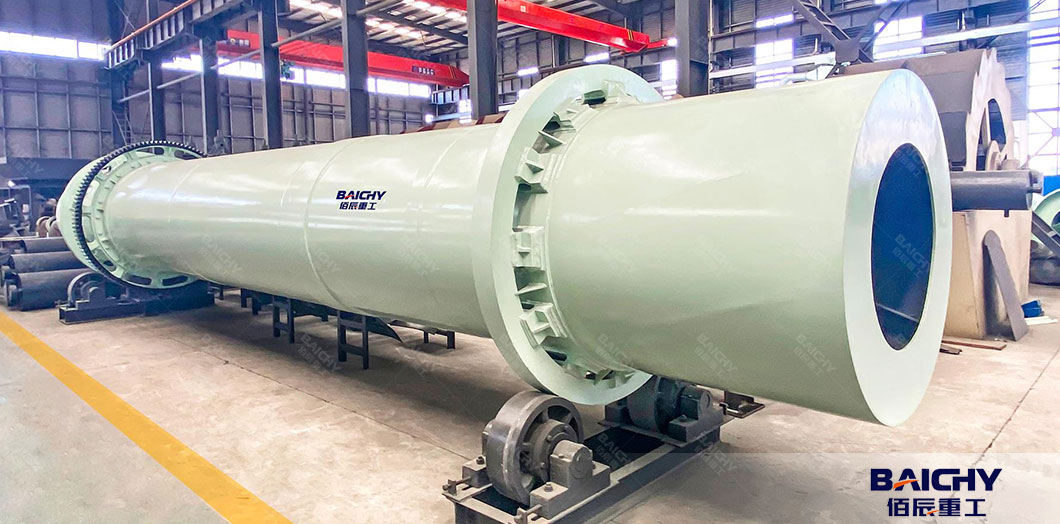
● Rotary Dryer:
- A rotating cylindrical drum heated by gas, steam, or electricity.
- Sand is tumbled inside the drum, exposing it to heat to reduce moisture to very low levels (<5%).
- Used when ultra-dry sand is required (e.g., for asphalt, foundry sand).

7. Material Handling & Storage Equipment
These machines move and store raw materials, intermediate products, and finished sand.
● Conveyor Belts:
- Transport sand between equipment (e.g., from feeder to crusher, screen to washer).
- Types include belt conveyors (most common), screw conveyors (for wet sand/slurries), and bucket elevators (for vertical transport).
● Silos:
- Large vertical storage tanks for finished sand.
- Equipped with discharge systems (e.g., augers, gates) to control the flow of sand during loading/unloading.
● Slurry Pumps:
- Move water-sand mixtures (slurries) from washers to dewatering equipment or wastewater treatment systems.
8. Wastewater Treatment Equipment
To recycle water and reduce environmental impact, plants include systems to treat wastewater from washing:
● Settling Tank (Clarifier):
- Allows suspended solids (fine sand, silt) in wastewater to settle to the bottom, while clear water is recycled for washing.
● Thickener:
- Concentrates fine solids from wastewater into a slurry, which can be dewatered (via filter press) and recovered as micro-sand.
● Filter Press:
- Further treats thickened sludge to produce dry solids (for disposal or reuse) and clean water for recycling.

Summary
The equipment in a sand processing plant works together to address key steps: feeding, crushing (for M-sand), screening, washing, impurity removal, dewatering, and storage. The combination depends on the raw material (natural vs. crushed), desired product quality, and environmental constraints (e.g., water availability). By integrating these machines, plants can produce consistent, high-quality sand for construction, industrial, and specialty applications.













 2026-01-05
2026-01-05


















 86-15093113821
86-15093113821
 86-15093113821
86-15093113821