Home
About us
Video
Service
Contact us
-
Mobile Crusher Plant
- Crawler Mobile Crusher
- Crawler Impact Crusher Plant
- Crawler Cone Crusher Plant
- Crawler Screening Plant
- Mobile Jaw Crusher Plant
- Mobile Impact Crusher Plant
- Mobile Cone Crusher Plant
- Mobile Crush and Screen Plant
- Mobile VSI Sand Making Plant
- Mobile Heavy Hammer Crusher Plant
- Mobile Concrete Crusher
- Modular Stone Crushing Plant
- Portable Stone Crusher
- Stone Crushing Machine
- Sand Making Machine
- Powder Grinding Mill
- Dressing Equipment
- Feeder & Screen
-
Stone Crusher Plant
- 40-60 tph Stone Crushing Plant
- Hard Stone Crusher Plant 80-100 tph
- 100-150 tph Stone Crusher Plant
- 100 tph Soft Stone Crusher Plant
- 180-220 tph Stone Crushing Plant
- 200-300 tph Stone Crusher Plant
- 200tph Stone Crusher Plant - Baichy Machinery
- 350-450 tph Stone Crusher Plant - Baichy Machinery
- 500tph Stone Crusher Plant - Baichy Machinery
- 800 tph Stone Crusher Plant - Baichy Machinery
- 1000 tph Stone Crusher Plant - Baichy Machinery
- Sand Making Plant
- Powder Grinding Mill Plant
- Beneficiation Plant
- Customer Case
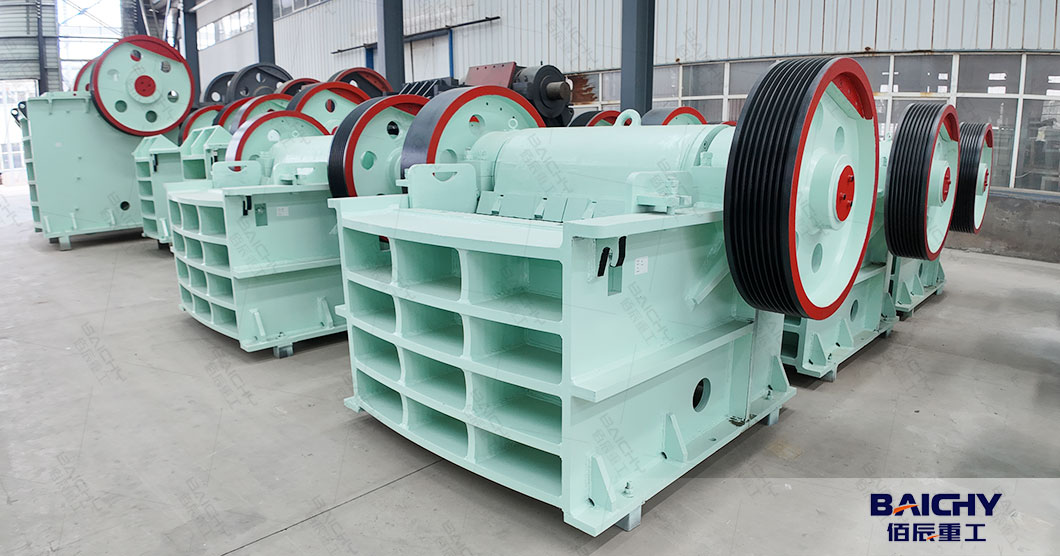
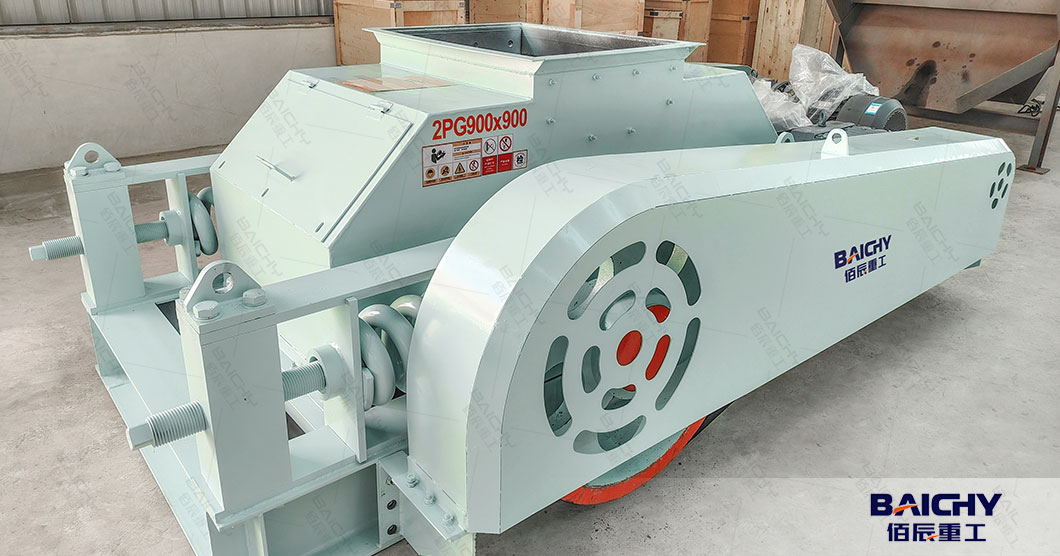
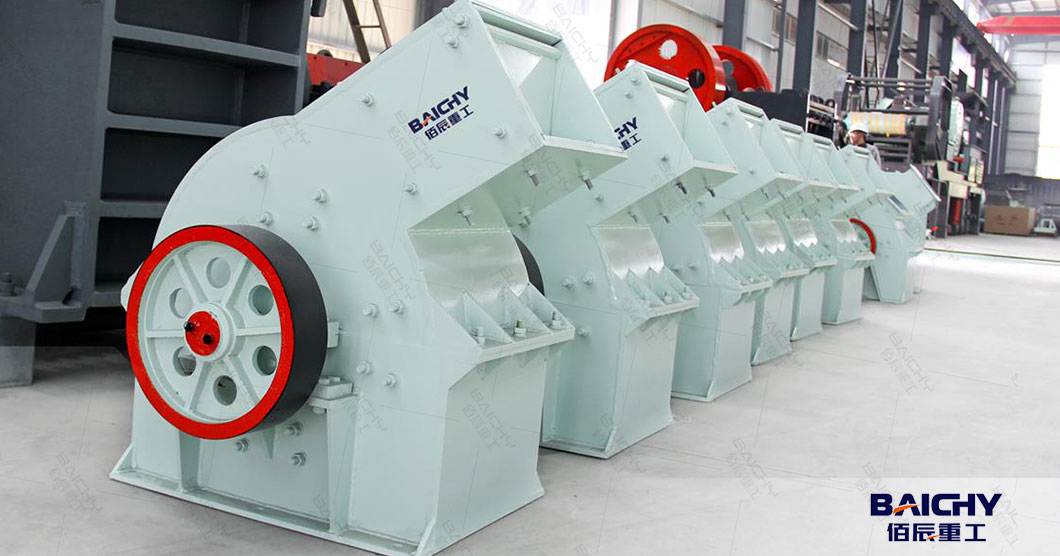






 2026-01-05
2026-01-05


















 86-15093113821
86-15093113821
 86-15093113821
86-15093113821