Mobile jaw crushers and mobile impact crushers are both widely used in mining, construction, and aggregate processing, but their design, working principles, and applications differ significantly. Below is a detailed comparison to help you understand their unique characteristics:
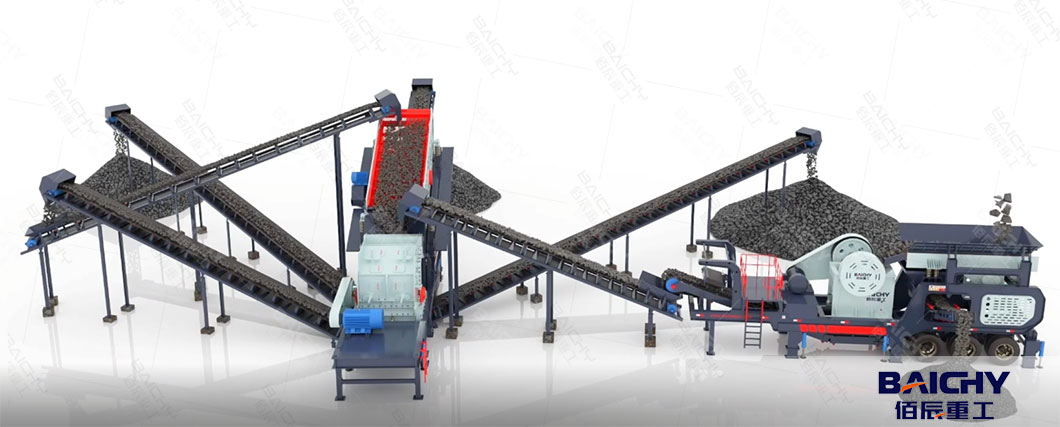

1. Working Principle: Crushing Mechanism
Mobile Jaw Crusher
- Crushing Principle: Uses a compression and shearing mechanism through the movement of a movable jaw plate against a fixed jaw plate.
- Process: Material is fed into the jaw cavity, and the movable jaw exerts pressure to crush the material by squeezing it against the fixed jaw, breaking it down through compressive force.
- Ideal for: Primary crushing of hard and abrasive materials.
Mobile Impact Crusher
- Crushing Principle: Relies on impact energy from a high-speed rotor with impact plates.
- Process: Material is thrown against impact plates by the rotor, breaking it through impact, and then particles are repeatedly crushed between the rotor and plates until they reach the desired size.
- Ideal for: Secondary or tertiary crushing of medium-hard to brittle materials.
2. Structural Design and Components
| Feature |
Mobile Jaw Crusher |
Mobile Impact Crusher |
| Crushing Chamber |
Vertical, V-shaped cavity with jaw plates |
Horizontal chamber with impact plates and rotors |
| Key Components |
Fixed jaw, movable jaw, toggle plate, eccentric shaft |
Rotor (with blow bars), impact plates, screening system |
| Wear-Resistant Parts |
Jaw plates, cheek plates |
Blow bars, impact plates, rotor tips |
| Mobility Configuration |
Often mounted on a tracked or wheeled chassis for rough terrain |
Wheeled chassis for easier road transport; some models have tracks |
3. Material Suitability
Mobile Jaw Crusher
- Preferred Materials: Hard, tough, and high-compressive-strength materials, such as: Granite, basalt, quartzite, Iron ore, gold ore, copper ore, Recycled concrete with hard aggregates
- Limitations: Less effective for soft or sticky materials, which may cause clogging.
Mobile Impact Crusher
- Preferred Materials: Medium-hard, brittle, and less abrasive materials, such as: Limestone, dolomite, gypsum, Construction waste (bricks, tiles) , Sandstone, coal
- Limitations: Not suitable for high-hardness materials (e.g., granite), as excessive wear on blow bars increases maintenance costs.
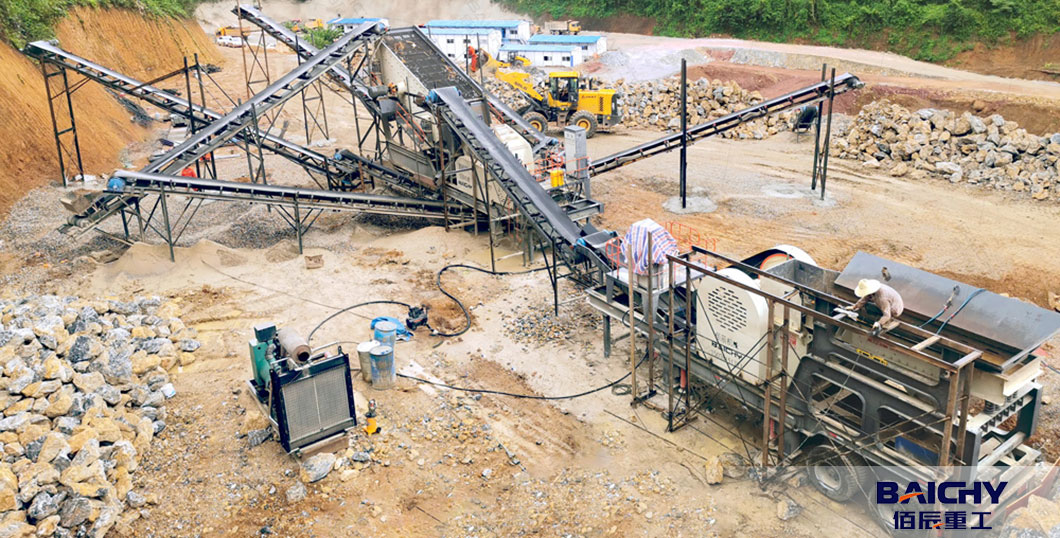

4. Output Particle Characteristics
Mobile Jaw Crusher
- Particle Shape: Cubic to angular, with a higher proportion of larger particles.
- Discharge Size: Typically 10–150 mm (adjustable via the jaw opening).
- Application: Primary crushing to produce coarse aggregates for road base or further processing.
Mobile Impact Crusher
- Particle Shape: More rounded and uniform, ideal for high-quality aggregate production.
- Discharge Size: Fine to medium (5–40 mm), adjustable via impact plate spacing or rotor speed.
- Application: Secondary crushing for concrete aggregates, asphalt materials, or sand production.
5. Mobility and Site Adaptability
Mobile Jaw Crusher
- Mobility Design:
- Tracked models excel in rough, off-road environments (mining sites, mountainous areas).
- Wheeled models are suitable for relatively flat sites but require auxiliary transport for long-distance moves.
- Setup Time: Quick to deploy, as primary crushing often occurs at the frontline of material extraction.
Mobile Impact Crusher
- Mobility Design:
- Commonly wheeled for easier transport between construction sites or quarries.
- Tracked models are available for complex terrains but are less common than jaw crushers.
- Setup Time: May require more time to adjust impact plates or install screening systems for precise particle control.
6. Energy Consumption and Maintenance
Mobile Jaw Crusher
- Energy Use: Lower power consumption for primary crushing, suitable for continuous operation.
- Maintenance:
- Jaw plates need replacement every 1,000–2,000 hours (depending on material hardness).
- Simple structure reduces downtime for repairs.
Mobile Impact Crusher
- Energy Use: Higher power consumption due to high-speed rotor operation, especially for hard materials.
- Maintenance:
- Blow bars and impact plates wear faster (replace every 500–1,000 hours for hard materials).
- Requires more frequent inspection of rotor balance and impact plate alignment.
7. Cost and Application Scenarios
Mobile Jaw Crusher
- Initial Cost: Lower investment for primary crushing equipment.
- Ideal Scenarios:
- Mining operations for primary ore crushing.
- Quarries producing coarse aggregates.
- Mobile recycling of hard concrete debris.
Mobile Impact Crusher
- Initial Cost: Higher investment due to complex rotor and impact plate systems.
- Ideal Scenarios:
- Construction sites needing high-quality, shaped aggregates.
- Sand production for concrete and asphalt.
- Recycling of bricks, tiles, and soft concrete.
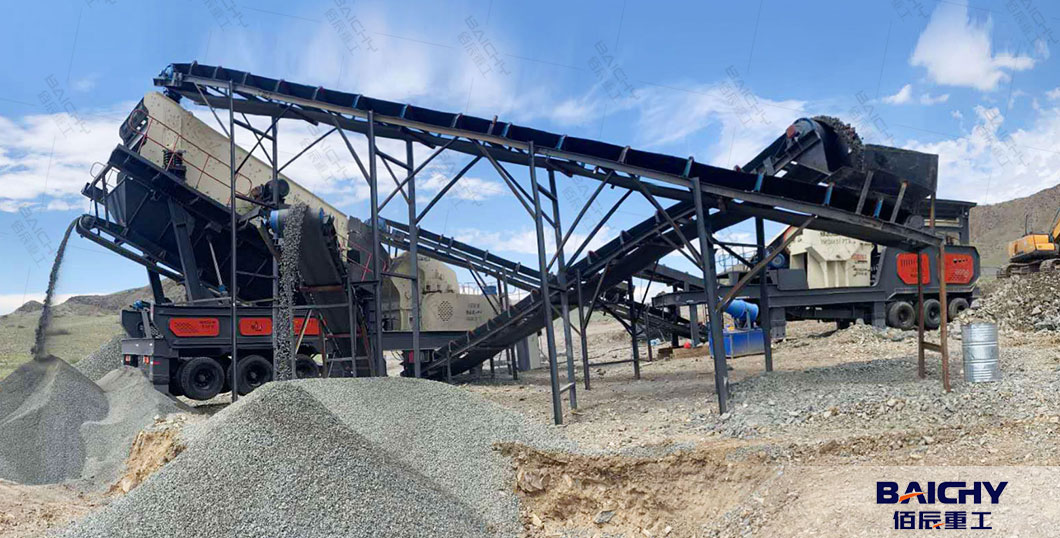

Conclusion: Which One to Choose?
Choose a Mobile Jaw Crusher if:
- You need primary crushing of hard materials (e.g., granite, ore).
- High durability and low maintenance are priorities.
- You operate in rough terrains requiring tracked mobility.
Choose a Mobile Impact Crusher if:
- You need fine crushing or shaping of medium-hard materials (e.g., limestone, construction waste).
- High-quality, rounded aggregates are essential for your project.
- You prioritize adaptability for secondary/tertiary crushing in construction sites.
Understanding these differences helps optimize equipment selection for efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and project-specific requirements. Always assess material properties, output specifications, and site conditions before making a decision.








 2026-01-06
2026-01-06


















 86-15093113821
86-15093113821
 86-15093113821
86-15093113821